As a passionate California Spangled cat breeder, one of the most important aspects of your job is to ensure that the kittens you produce are healthy and genetically sound. This is where genetic testing comes in – a process that can help you identify any potential health concerns your cats may have before breeding. If you’re new to genetic testing, you might be wondering what it entails, why it’s necessary, and how to go about arranging it for your cats – and that’s exactly what we’ll be exploring in this complete guide to genetic testing options for California Spangled cats. So, let’s dive right in!
What is Genetic Testing?

Genetic testing is a medical examination that helps individuals determine if they carry certain genetic traits or disorders. While most people associate this type of testing with human health, genetic testing for pets, including California Spangled cats, is becoming more common. Genetic testing for cats is a beneficial tool for predicting and preventing genetic disorders, identifying health risks associated with breeding, and gaining valuable information about the cat’s ancestry. In this section, we will dive into the importance of genetic testing for California Spangled cats and how it can help breeders produce healthy and genetically sound offspring. To learn more about California Spangled cat genetics, their health concerns, and breeding tips, check out our related articles linked below.
Why Genetic Testing is Important for Breeding California Spangled Cats
Breeding California Spangled Cats can be a joy for cat-lovers, but it is essential to ensure that the kittens born are healthy and free from genetic diseases. This is where genetic testing comes in, as it helps breeders determine the genetic makeup of their cats and identify any potential health concerns that may be passed down to their offspring.
Genetic testing is important for breeding California Spangled Cats for the following reasons:
- It ensures that the cats are healthy and free from genetic disorders that could be passed on to their offspring. This reduces the risk of kittens being born with genetic diseases, which can be expensive and difficult to treat.
- It helps identify carriers of genetic diseases, which means that breeding can be avoided between two cats that both carry a particular genetic disorder.
- It can give breeders insight into the genetic traits of their cats, such as coat colors and patterns, which can inform breeding decisions to ensure that desirable traits are passed down to their offspring.
- It can help breeders avoid inbreeding, which can cause genetic defects and other health issues in future generations.
By getting their California Spangled Cats genetically tested, breeders can make more informed breeding decisions and reduce the risk of producing kittens with genetic disorders. This ensures a healthier and happier breeding program and helps preserve the breed’s genetic diversity for generations to come. Whether a breeder is new to breeding or an experienced breeder, genetic testing is an essential step to take before bringing cats together to produce a litter of kittens.
To learn more about California Spangled Cat genetics and breeding tips, check out our other articles on California Spangled Cat genetics, California Spangled Cat breeding tips, and the impact of inbreeding on California Spangled Cat breeding. You can also explore our article on genetic disorders in California Spangled Cats to learn more about the specific diseases that breeders should test for before breeding their cats.
Understanding DNA Testing
DNA testing is a process of analyzing an animal’s genetic material to identify specific genetic traits, mutations, and markers. It involves obtaining a DNA sample, usually from a blood or cheek swab, and submitting it for laboratory analysis. DNA testing has become an essential tool in breeding California Spangled Cats because it allows breeders to select cats with desirable genetic traits and avoid breeding cats with inheritable health issues or disorders. Here are some key points to understand about DNA testing:
- Genes: Genes are the basic units of heredity that determine an animal’s traits, such as coat color and pattern, eye color, and disposition.
- Genetic mutations: Genetic mutations are alterations in the DNA sequence that can lead to changes in an animal’s traits. Some mutations can be beneficial, whereas others can cause hereditary diseases and disorders.
- Markers: Genetic markers are specific sequences of DNA that can be used to identify and track an animal’s genetic material. They are often used in pedigree analysis to trace the ancestry of a particular cat or breed.
- SNPs: SNPs, or single nucleotide polymorphisms, are the most common type of genetic variation in animals. They involve a single nucleotide change at a specific location in the DNA sequence and can be used to identify specific traits or mutations.
By understanding the basics of DNA testing, breeders can make informed decisions about which cats to breed based on their genetic makeup and potential offspring. It is essential to keep accurate records of all DNA testing results and pedigree information to track breeding traits and avoid potential health issues in future litters. For more information on California Spangled Cat breeding traits, see our article on California Spangled Cat Breeding Traits, or learn about the importance of pedigree analysis in breeding on our page about California Spangled Cat Pedigree.
Common California Spangled Cat Health Concerns to Test For

As a responsible breeder, it’s essential to ensure that your California Spangled cats are healthy and free from genetic disorders. While California Spangled cats are generally robust and healthy, like any other breed, they are prone to certain health concerns. It’s crucial to carry out genetic testing to identify any predispositions your cat may have or be carrying. In this section, we’ll discuss the common California Spangled cat health concerns that you should test for before breeding. Let’s dive into it.
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM)
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a common heart disease among cats, and California Spangled Cats may be at risk for developing this condition. HCM is a genetic condition that affects the heart muscles, causing them to thicken and become stiff. This can lead to a range of symptoms, from mild to severe, and in some cases can be fatal.
What are the signs of HCM in California Spangled Cats?
In the early stages of HCM, your California Spangled Cat may show no symptoms at all. However, as the condition progresses, you may notice a range of signs that indicate a problem with your cat’s heart. These can include:
– Difficulty breathing
– Shortness of breath
– Lethargy or weakness
– Fainting or collapsing
– Coughing or wheezing
– Heart murmurs or irregular heartbeats
How is HCM diagnosed in California Spangled Cats?
If you suspect that your California Spangled Cat may have HCM, it’s important to bring him or her to a veterinarian for a full examination. Your vet will listen to your cat’s heart, check for any abnormal rhythms or murmurs, and may recommend additional tests to confirm a diagnosis. These can include:
– Echocardiogram: This is an ultrasound of the heart that allows your vet to see the thickness of the heart walls and how well the heart is functioning.
– X-rays: These can help your vet to see any abnormalities or enlargement of the heart on a radiograph.
– Blood tests: These can be used to check for any other underlying health conditions that may be contributing to your cat’s symptoms.
How is HCM treated?
Unfortunately, there is no cure for HCM in cats, but there are treatments available that can help to manage the condition and improve your cat’s quality of life. These can include:
– Medications: There are a number of medications that can be used to help manage HCM in cats, including beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers.
– Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be recommended to remove a portion of the thickened heart muscle.
– Lifestyle changes: In some cases, making simple changes to your cat’s diet and exercise routine, as well as reducing stress in the home environment can have a positive impact on your cat’s heart health.
How can genetic testing help?
Genetic testing can help to identify if your California Spangled Cat carries the gene for HCM, and can inform breeding decisions to reduce the risk of passing on the gene to future generations. It is recommended that all cats used for breeding undergo genetic testing for HCM, as well as other common genetic conditions. This can help to ensure the health and well-being of the breed.
Progressive Retinal Atrophy (PRA)
Progressive Retinal Atrophy (PRA) is a genetic disorder that causes the gradual deterioration of the retina, leading to eventual blindness. This condition affects many breeds of cats, including California Spangled Cats. It is important to test for PRA before breeding California Spangled Cats to ensure that the kittens do not inherit the condition.
What is PRA?
PRA is a genetic disease that affects the retina, which is responsible for converting light into electrical signals that are transmitted to the brain. As the condition worsens, the retina degenerates, ultimately leading to complete blindness. Unfortunately, there is no cure for PRA, so it is important to prevent the condition from being passed on to future generations.
How Is PRA Inherited?
PRA is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder, meaning that both parents must carry a copy of the mutation for their offspring to develop the condition. Cats with only one copy of the mutation will not have symptoms but will be carriers and can pass the mutation on to their offspring.
Testing for PRA
There are several genetic tests available for PRA in cats. These tests look for specific mutations in the cat’s DNA that are associated with the disorder. The most common test looks for a mutation in the CEP290 gene, which is known to cause PRA in many breeds of cats.
If a cat is found to have two copies of the mutation, it is recommended that they not be bred. However, if the cat only has one copy of the mutation, they can still be bred, but it is important to choose a mate that does not carry the mutation to reduce the likelihood of passing the condition on to their offspring.
Below is a table that summarizes the possible results of PRA testing:
| Test Result | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| Normal/Non-Carrier | The cat does not have a mutation associated with PRA and will not develop or pass on the condition |
| Carrier | The cat has one copy of the mutation associated with PRA and may pass it on to their offspring, but will not develop the condition themselves |
| Affected | The cat has two copies of the mutation associated with PRA and will develop the condition and pass it on to all of their offspring |
Conclusion
PRA is a serious genetic disorder that can lead to complete blindness in California Spangled Cats. By testing for the mutation associated with PRA, breeders can prevent the condition from being passed on to future generations and ensure the health of their kittens. It is important to work with a veterinarian or breeder to arrange genetic testing before breeding California Spangled Cats.
Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD)
Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) is a genetic disorder that affects cats and can lead to renal failure. PKD is characterized by the growth of cysts in the kidneys, which can cause the kidneys to enlarge and lose function over time. The disease is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, which means that a cat with one copy of the mutated gene is affected by the disease.
Signs and Symptoms of PKD
– Increased thirst and urination
– Weight loss
– Vomiting
– Decreased appetite
– Lethargy
– Blood in the urine
PKD Testing for California Spangled Cats
PKD is a relatively common disease in cats, including California Spangled Cats. It is essential to test breeding cats for this disease to prevent it from being passed down to future generations. The most commonly used method to identify PKD in cats is through ultrasound examination. PKD cats have large, irregularly-shaped kidneys with multiple cysts visible on ultrasound. DNA testing is also available, which can confirm if a cat is carrying the PKD gene.
Preventing PKD in California Spangled Cats
Breeding cats that are confirmed carriers of the PKD gene should not be bred with other carriers to prevent the disease from being passed down. Instead, carriers should only be bred with cats that do not carry the gene, and all offspring should be tested for PKD before being used for breeding. By following this process, breeders can eliminate PKD from their breeding program and prevent it from being passed on to future generations of California Spangled Cats.
Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency (PKDef)
Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency (PKDef) is a genetic disorder that affects California Spangled cats. It is caused by a deficiency in the Pyruvate Kinase enzyme, which is responsible for producing energy in red blood cells. This deficiency can lead to anemia, lethargy, and even death in severe cases.
Symptoms of PKDef in California Spangled Cats
Some symptoms that may indicate PKDef in California Spangled cats include:
- Weakness and lethargy
- Loss of appetite and weight loss
- Pale gums
- Jaundice
- Fever
- Irregular breathing
- Increased heart rate
- Enlarged spleen and liver
If you notice any of these symptoms in your California Spangled cat, it is important to take them to a veterinarian for testing.
PKDef Testing Methods
There are various DNA testing methods available to determine if a California Spangled cat has PKDef. These tests are typically done through a blood sample, cheek swab, or saliva sample.
PKDef Inheritance
PKDef is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder, which means that a cat must inherit two copies of the PKDef gene (one from each parent) in order to develop the condition. If a cat inherits only one copy of the gene, they will be a carrier but will not show any symptoms.
Preventing PKDef in Breeding
To prevent the transmission of PKDef from parent cats to their offspring, it is important to test both cats for the gene. If both parent cats are carriers or affected by PKDef, breeding them together should be avoided. If one parent cat is a carrier and the other is clear, their offspring will have a 50% chance of being a carrier but will not be affected by the disorder. If both parent cats are clear, their offspring will not inherit the disorder.
PKDef is a serious genetic disorder that affects California Spangled cats and can lead to severe health complications. By getting your cat tested and taking appropriate breeding precautions, you can help prevent the transmission of this disorder and ensure the health of future generations of California Spangled cats.
Feline Leukemia Virus (FeLV) and Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV)
Genetic testing can also help determine if a California Spangled cat is carrying Feline Leukemia Virus (FeLV) or Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV). These viruses can be detrimental to a cat’s health and can even be fatal. While neither virus is exclusive to California Spangled cats, all cats are at risk of being exposed to these viruses.
Feline Leukemia Virus (FeLV) is a retrovirus that can suppress a cat’s immune system, increasing their susceptibility to other illnesses. FeLV can also cause anemia and cancer. The virus is primarily spread through contact with infected cats, such as sharing food and water bowls or through mutual grooming. Kittens can also contract the virus in utero or through their mother’s milk.
Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV), also known as feline AIDS, weakens a cat’s immune system by attacking white blood cells. This can lead to a wide range of symptoms, including weight loss, oral infections, and chronic respiratory infections. The virus is primarily spread through bite wounds from infected cats during fights or mating.
Testing for FeLV and FIV involves a blood draw from the cat, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. The test determines whether the cat has been exposed to either virus, and if so, whether they are actively infected or have only been exposed but are not currently ill. If a cat tests positive for either virus, they will require lifelong management to minimize symptoms and reduce the risk of spreading the infection to other cats.
It is essential to test all California Spangled cats for FeLV and FIV before breeding. If a cat tests positive for either virus, they should not be bred as the viruses can be passed down to their offspring. Additionally, breeding an infected cat can further spread the virus to other cats in the breeding community and potentially harm the breed’s overall health.
Here’s a table summarizing some key information about FeLV and FIV:
| Virus | Spread | Symptoms | Testing | Management |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeLV | Contaminated food, water, mutual grooming, in utero, or through milk | Anemia, cancer, weakened immune system | Blood test | Lifelong management, minimize symptoms |
| FIV | Bite wounds from infected cats during fights or mating | Weight loss, oral infections, chronic respiratory infections | Blood test | Lifelong management, minimize symptoms |
Testing for Coat Colors and Patterns
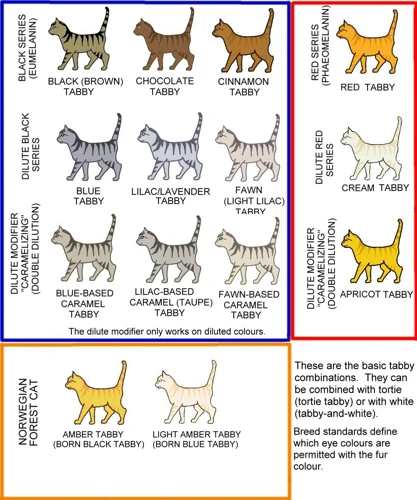
As fascinating as it is to know about the potential health problems that a California Spangled Cat may face, it is equally important to discuss their striking coat colors and patterns. If you’re looking to breed these gorgeous felines, it’s important to understand the genetics behind their coat, which can affect the likelihood of certain patterns and colors appearing in offspring. In this section, we’ll break down the science behind coat colors and patterns, and explore the different testing options available for breeders. Let’s dive in.
The Genetics of California Spangled Cat Coat Colors and Patterns
The California Spangled Cat is a beautiful breed with a striking coat that comes in different colors and patterns. The genetics of these cats’ coat can be complex, with multiple genes interacting to give different variations. Understanding the genetics of coat colors and patterns in California Spangled Cats can help breeders make informed decisions when breeding for specific traits.
One of the most distinct coat patterns in California Spangled Cats is the spotted pattern. This is a dominant trait, meaning that only one copy of the gene is needed for a cat to exhibit the spotted pattern. The spotted pattern is often accompanied by a tabby pattern, with stripes on the legs, tail, and head.
Another coat pattern in California Spangled Cats is the mackerel tabby pattern. This pattern is characterized by narrow, ticked stripes running parallel to the spine. The mackerel tabby pattern is also a dominant trait.
The ticked tabby pattern is another variant of the tabby pattern seen in California Spangled Cats. This coat pattern is characterized by darker spots on a lighter background, giving a speckled appearance. The underlying genetics of this pattern are not yet fully understood.
There are also different coat colors in California Spangled Cats, including black, brown, silver, and red. The underlying genetics of coat color are also complex, with multiple genes involved in determining the final color.
To better understand the genetics of coat colors and patterns in California Spangled Cats, take a look at the following table:
| Gene | Coat Trait | Description |
|---|---|---|
| P | Coat Color | Determines whether a cat has a black or red coat. Cats with two copies of the dominant P gene (PP) will have a black coat, while cats with two copies of the recessive p gene (pp) will have a red coat. Cats with one copy of each (Pp) will also have a black coat. |
| B | Brown Coat Color | Determines whether a cat has a black or brown coat color. Cats with two copies of the dominant B gene (BB) or one copy of the dominant B gene and one copy of the recessive b gene (Bb) will have a black coat. Cats with two copies of the recessive b gene (bb) will have a brown coat. |
| SILV | Silver Coat Color | Determines whether a cat will have a silver or non-silver coat. Cats with two copies of the dominant SILV gene (SILV/SILV) will have a silver coat. Cats with one copy of the dominant SILV gene and one copy of the recessive non-silver gene (SILV/ns) may display varying degrees of silvering. Cats with two copies of the non-silver gene (ns/ns) will have a non-silver coat. |
| Sp (tabby) | Tabby Pattern | Determines whether a cat will display a tabby pattern. The dominant Sp gene is responsible for the spotted tabby pattern, while the recessive sp gene produces an unpatterned coat. |
| Ta (tabby) | Tabby Pattern | Determines the type of tabby pattern displayed. The dominant Ta gene produces a classic or blotched tabby pattern, while the recessive ta gene produces a mackerel tabby pattern. |
As a breeder, understanding the genetics of coat colors and patterns can help you make informed decisions when selecting breeding pairs. By using genetic testing, you can identify the specific genes present in your cats and make better breeding decisions to achieve desired traits in future litters.
Coat Color and Pattern Testing Options
If you’re interested in breeding California Spangled Cats for their unique coat colors and patterns, it’s important to conduct coat color and pattern testing in addition to health testing. This will help ensure that you’re producing healthy and visually stunning kittens.
Here are some coat color and pattern testing options to consider:
- Agouti Testing: This test examines the agouti gene, which determines whether a cat has banded hair (agouti) or solid-colored hair. It is important to know whether your California Spangled Cat carries this gene if you plan on breeding for ticked coats.
- Dilution Testing: This test examines the dilution gene, which can cause coat colors to become lighter and more muted. Dilution testing is important if you plan on breeding for lighter coat colors.
- Colorpoint Testing: This test examines the presence of the colorpoint gene, which produces the distinctive pointed patterns seen in Siamese cats. If you’re interested in breeding for pointed patterns, it’s important to know whether your California Spangled Cat carries this gene.
- Tabby Testing: This test examines the tabby gene, which produces striped, blotched, or spotted patterns on a cat’s coat. Knowing whether your California Spangled Cat carries this gene can help you produce visually stunning kittens with unique tabby patterns.
It’s important to note that some coat colors and patterns in California Spangled Cats are rarer than others, so it’s important to do your research and find a reputable DNA testing laboratory that offers a range of coat color and pattern tests. By conducting coat color and pattern testing, you can ensure that you’re producing kittens with the desired coat colors and patterns while maintaining the health of the breed.
How to Arrange Genetic Testing for Your California Spangled Cat
As a responsible breeder or California Spangled cat owner, arranging genetic testing for your feline companion is crucial. Not only can genetic testing provide essential information about potential health concerns and coat color patterns, but it can also aid in making informed breeding decisions. However, the process of arranging genetic testing may seem overwhelming. In this section, we will explore the steps involved in arranging genetic testing for your California Spangled cat. From consulting with a veterinarian or breeder to interpreting results and discussing breeding options, we’ve got you covered.
Consulting with a Veterinarian or Breeder
When it comes to arranging genetic testing for your California Spangled cat, consulting with a veterinarian or breeder is an important first step. A veterinarian can provide you with information about the different types of genetic tests available and which tests are relevant for your cat’s breed and specific health concerns. They can also perform physical exams to check your cat’s overall health and rule out any underlying health conditions.
On the other hand, a breeder can be an excellent resource for genetic testing options. They can advise you on the most appropriate tests to run based on the breed standard, previous health conditions in your cat’s lineage, and the specific traits you would like to breed for. Additionally, many breeders have established relationships with DNA testing laboratories and can recommend reputable providers.
Before consulting with a veterinarian or breeder, it is important to prepare a list of questions to ensure that you get all the information you need. Consider asking about:
- Which genetic tests are recommended for California Spangled cats before breeding?
- What is the turnaround time for test results?
- How accurate are the test results?
- What are the costs associated with each test?
- Are there any alternative testing options available?
- How do I interpret the test results and what breeding decisions should be made based on the results?
By consulting with an expert and asking the right questions, you can make informed decisions about which genetic tests to pursue for your California Spangled cat. This can help to ensure the health and well-being of your cat and any offspring they may produce.
Selecting a DNA Testing Laboratory
When it comes to selecting a DNA testing laboratory to perform genetic testing on your California Spangled cat, there are a few factors to consider.
Accreditation: It is important to choose a laboratory that is accredited by a recognized accreditation organization, such as the American Association for Laboratory Accreditation (A2LA) or the College of American Pathologists (CAP). This ensures that the laboratory follows strict quality standards in their testing processes.
Testing Options Available: Different laboratories may offer different testing options for California Spangled cats. It is important to select a lab that offers the specific tests you are interested in for your cat.
Turnaround Time: The amount of time it takes for the laboratory to provide your results can vary. Some labs may offer expedited testing for an additional fee. Consider the timeline you are working with and choose a lab with a turnaround time that works for you.
Cost: The cost of testing can vary between laboratories. Consider the cost of the specific tests you need for your cat and compare prices between different labs.
Customer Support: It is important to select a laboratory with a responsive customer support team. This can be helpful if you have questions about the testing process or need assistance interpreting your results.
Some popular DNA testing laboratories for cats include Wisdom Panel, Optimal Selection, and BasePaws. Do your research and compare options to select the best lab for your California Spangled cat’s genetic testing needs.
Interpreting Genetic Testing Results
After conducting genetic testing on your California Spangled cat, it’s important to understand how to interpret the results. Genetic testing can reveal whether a cat carries certain genes for health concerns or coat color/patterns. Below is a table explaining some common genetic testing results and their meanings:
| Genetic Result | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Negative/Norm | The cat does not carry the gene in question and will not pass it on to offspring. |
| Positive | The cat carries one copy of the gene in question and has a chance of passing it on to offspring. Breeding with another positive cat for the same gene increases the likelihood of offspring inheriting two copies of the gene, which can result in health concerns or desired coat color/patterns. |
| Heterozygous (carrier) | The cat carries one copy of the gene in question but does not exhibit any health concerns or changes to coat color/patterns. Breeding with another carrier increases the likelihood of offspring inheriting two copies of the gene, which can lead to health concerns or desired coat color/patterns. |
| Homozygous (affected) | The cat carries two copies of the gene in question and exhibits health concerns or changes to coat color/patterns. Breeding with another homozygous cat will result in offspring inheriting two copies of the gene, which can lead to severe health concerns or desired coat color/patterns. |
It’s important to note that genetic testing results should always be interpreted by a veterinarian or genetic counselor. They can help explain the significance of the results and guide breeders in selecting breeding options to avoid producing offspring with health concerns or undesired coat color/patterns.
Discussing Breeding Options Based on Results
After receiving the results of genetic testing for your California Spangled cat, it’s important to discuss the breeding options available based on the results. This discussion should take place with your veterinarian or a reputable breeder. They can help you understand the test results and develop a breeding plan that will prioritize the health and wellbeing of your cat.
The breeding options available will depend on the specific genetic traits that were tested for. To make it easier to understand the results, we’ve created a table outlining possible genetic test results and the corresponding breeding options:
| Test Results | Breeding Options |
|---|---|
| Normal | These cats can be bred without restrictions. |
| Carrier | These cats carry one copy of the gene mutation for a particular disease, but the disease does not manifest in them. They can be bred to normal cats or other carriers, but not to affected cats to avoid producing affected offspring. |
| Affected | These cats have two copies of the gene mutation for a particular disease, one inherited from each parent. They should not be bred to avoid passing on the disease to their offspring. |
Of course, it’s important to remember that breeding decisions should not be made based on genetic testing results alone. It’s also important to consider the cat’s overall health, temperament, and breed standards when choosing a mate.
If you’re working with a breeder, they may have their own policies in place regarding breeding options for cats with certain genetic results. It’s important to have a clear understanding of these policies before committing to a breeding arrangement.
Genetic testing can provide valuable information when it comes to breeding California Spangled cats. It’s important to discuss the results with a veterinarian or breeder and carefully consider breeding options based on those results and other factors. By doing so, you can help ensure the health and longevity of future generations of California Spangled cats.
Conclusion
After considering the various genetic testing options available for California Spangled cats, it’s clear that testing is a crucial step for any responsible breeder. By understanding the DNA makeup of your breeding cats, you can minimize the risk of passing on genetic diseases to their offspring, and also choose the best possible breeding partners to improve the breed’s overall genetic health.
When it comes to health concerns, testing for Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM), Progressive Retinal Atrophy (PRA), Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD), and Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency (PKDef) is highly recommended. In addition, testing for Feline Leukemia Virus (FeLV) and Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV) is crucial to ensure that your breeding cats are healthy in all respects.
Coat color and pattern testing may not be as essential, but it’s still helpful for breeders who want to produce specific coat colors or patterns. Understanding the genetics behind coat colors and patterns is essential, and there are various DNA testing options available to help breeders achieve their goals.
It’s important to note that arranging genetic testing for your California Spangled cat requires careful research and consideration. Consulting with your veterinarian or breeder is a must, and selecting a reputable DNA testing laboratory is crucial for accurate results. Interpreting the results and discussing breeding options based on those results is the final step in the process.
Overall, genetic testing is an essential aspect of responsible breeding, and with the right approach, breeders can ensure the health and genetic diversity of their California Spangled cats for generations to come. By taking the time to understand DNA testing and all the options available, breeders can work towards producing healthy, happy, and genetically diverse cats.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of genetic testing for California Spangled Cats?
The purpose of genetic testing for California Spangled Cats is to identify any potential health concerns or genetic abnormalities that may be passed down to offspring. This can help breeders make informed decisions and improve the overall health of the breed.
What are some common health concerns for California Spangled Cats?
California Spangled Cats may be at risk for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, progressive retinal atrophy, polycystic kidney disease, pyruvate kinase deficiency, and feline leukemia virus/feline immunodeficiency virus. Genetic testing can identify if a cat is a carrier for any of these conditions.
Why should breeders test for coat colors and patterns?
Breeders may choose to test for coat colors and patterns to get a better understanding of their cat’s genetic makeup. This can help them make more informed breeding decisions and produce desired coat colors or patterns in offspring.
Can genetic testing prevent health problems in California Spangled Cats?
While genetic testing cannot prevent health problems, it can help breeders make informed decisions that can reduce the risk of passing down genetic abnormalities to offspring. Early detection of potential health concerns can also lead to earlier treatment and better outcomes.
How is DNA testing performed on California Spangled Cats?
DNA testing is usually performed with a cheek swab or blood sample. The sample is sent to a laboratory, where it is analyzed for specific genetic markers or mutations associated with health concerns or coat colors and patterns.
How long does it take to get genetic testing results?
The duration of genetic testing results may vary depending on the specific laboratory used and the type of test being performed. Generally, results can be expected within a few weeks to a month.
What should breeders do with the results of genetic testing?
Breeders should use the results of genetic testing to make informed breeding decisions. For example, if a cat tests positive for a specific health concern, a breeder may choose to not breed that cat or only breed it with a partner that tests negative.
Is genetic testing expensive for California Spangled Cats?
The cost of genetic testing can vary depending on the specific test being performed and the laboratory used. However, most genetic tests are moderately priced and will likely vary between $100-$300.
Can genetic testing identify the gender of a California Spangled Cat?
No, genetic testing cannot identify the gender of a cat. Gender is determined by the cat’s reproductive organs, which are visible and easily identifiable.
Is genetic testing necessary for all California Spangled Cats?
While genetic testing is not necessary for all California Spangled Cats, it is recommended for cats that will be used for breeding purposes. Additionally, breeders may choose to test cats for coat color and pattern genes.







